How to Access 10.10.0.1 Admin Settings Easily for Efficient Network Management
Accessing the 10.10.0.1 admin settings allows users to manage their router’s network, including changing the WiFi password, adjusting security settings, and customizing other options. To access these settings, a user simply needs to open a web browser and enter “http://10.10.0.1” in the address bar, then log in using the default or personalized username and password.
If the login page does not appear, it may help to check the device’s IP address using command prompt or network settings to confirm the correct gateway address. Resetting the router might also be necessary if the user cannot access the admin page due to forgotten credentials or other issues.
Understanding this process provides direct control over the network and can improve connectivity and security. This guide will explain each step clearly, ensuring anyone can follow along without technical difficulty.
Accessing 10.10.0.1 Admin Settings

Accessing the 10.10.0.1 admin settings involves first finding the correct IP address on the device. After this, the user needs to log in with proper credentials. If problems happen during connection, there are specific steps to fix them.
Locating the Default Gateway
The default gateway is usually the IP address you use to access router settings. On Windows, users can find it by opening Command Prompt and typing ipconfig. The line labeled “Default Gateway” shows the IP, which should be 10.10.0.1 if that is correct for the router.
On a Mac, users open Terminal and type netstat -nr | grep default or route get default. The result will show the gateway IP address. Make sure the device is connected to the router via Wi-Fi or Ethernet before checking.
This step confirms the address used to access the router’s admin panel.
Logging In to the Admin Panel
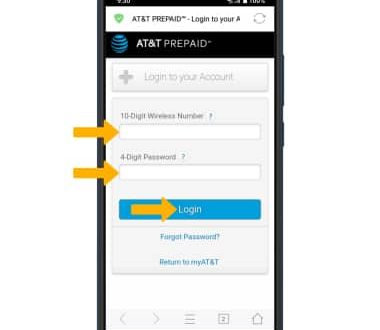
Open a web browser and type http://10.10.0.1 into the address bar. Press Enter to go to the login page. The page prompts for a username and password.
Default credentials are often “admin” for both username and password, but these may vary by router model. If the credentials were changed, the user must use those. It’s best to check the router label or manual for the default username and password.
After entering the details, click the Login button. Once logged in, users can change settings such as Wi-Fi name, password, and security options.
Troubleshooting Connection Issues
If the browser does not load the login page, check these steps:
- Confirm the device is connected to the router’s network.
- Ensure 10.10.0.1 is correct by checking the default gateway.
- Try using another browser or clearing the browser cache.
- Restart the router and the device attempting to connect.
If none of these work, try resetting the router to factory settings. This often restores the default IP and login credentials but will erase custom settings.
Managing Router Configuration
Configuring a router requires careful attention to security and network performance. Key tasks include securing access, adjusting settings to fit user needs, and ensuring the firmware is up to date without risking device stability.
Changing the Admin Password
Changing the admin password is essential to prevent unauthorized access. The user must log in to the router’s admin page by entering the IP address (such as 10.10.0.1) in a browser.
Once logged in, the admin password can be found under Account Settings or Security. The new password should be strong, combining uppercase letters, numbers, and symbols, at least eight characters long.
It is important to avoid default passwords or easily guessed options like “admin” or “password.” After changing, save the settings and log out. This step secures the router from basic hacking attempts.
Customizing Network Settings
Router users can customize the network name (SSID) and WiFi password to identify their network uniquely. This is done in the Wireless or WiFi Settings section.
They can also set parental controls, guest networks, and manage connected devices from this area. Adjusting the firewall settings helps control incoming and outgoing traffic for better security.
When changing WiFi passwords, it is recommended to use WPA2 or WPA3 encryption for stronger protection. Saving these settings usually requires a router restart.
Updating Firmware Securely
Firmware updates improve performance and patch security issues. Users should always check the router manufacturer’s official website or admin page for updates linked to their model.
Before updating, writing down current settings is useful in case the update resets the router to factory defaults. Users should avoid interrupting the update process, such as powering off the device, to prevent permanent damage.
Updates should be done over a wired connection if possible, as wireless connections may disconnect during the update, causing failures. After completion, verifying the firmware version confirms a successful update.